A molecule of a greenhouse gas has more of a warming influence when the gas is rarer;4 rows Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climateThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it
The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
Amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
Amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere-8 rows Greenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon AtmosphericAnd the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases is continuing to increase




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
Greenhouse Gases Methane, Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 3% A man scavenges for waste to recycle at a garbage dump in Linfen, China Landfill sites like this produce greenhouse gases because rotting organic waste like food waste emits methane which warms the atmosphere unless it is capturedSince the Industrial Revolution in the late 1700s and early 1800s, people have been releasing large quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere That amount has skyrocketed in the past century Greenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by By volume, the dry air in Earth's atmosphere is about 7809 percent nitrogen, 95 percent oxygen, and 093 percent argon A brew of trace gases accounts for the other 003 percent, including the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and ozone
The effect of greenhouse gases There are five gases of human origin that contribute most – together up to 95% of the total – to the increase in global warming Here you will discover the source of their emission, the time they spend in the atmosphere and what percentage they contribute to the greenhouse effectThe excess of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is triggering harmful global warming, so reducing the amount of these gases should help to tackle climate change This can be done in two ways lower the emissions we are sending into the atmosphere, from activities such as industrial processes, power generation, transport and intensive agriculture The majority of greenhouse gases come from burning fossil fuels to produce energy, although deforestation, industrial processes, and some agricultural practices also emit gases into the atmosphere Greenhouse gases act like a blanket around Earth, trapping energy in the atmosphere and causing it to warm This phenomenon is called the greenhouse
Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that produce the greenhouse effect Changes in the concentration of certain greenhouse gases, from human activity (such as burning fossil fuels), increase the risk of global climate change Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, nitrous oxide, halogenatedGreenhouse gases like carbon dioxide exist in our atmosphere They are called greenhouse gases because they cause the atmosphere to act like the glass of greenhouse That is, the sun's rays pass through the atmosphere and heat up the earth, and then the greenhouse gases prevent the heat from leaving Methane gas emitted by cows and other livestock does have a significant impact on the amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere, which are the main culprits behind climate change and global



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
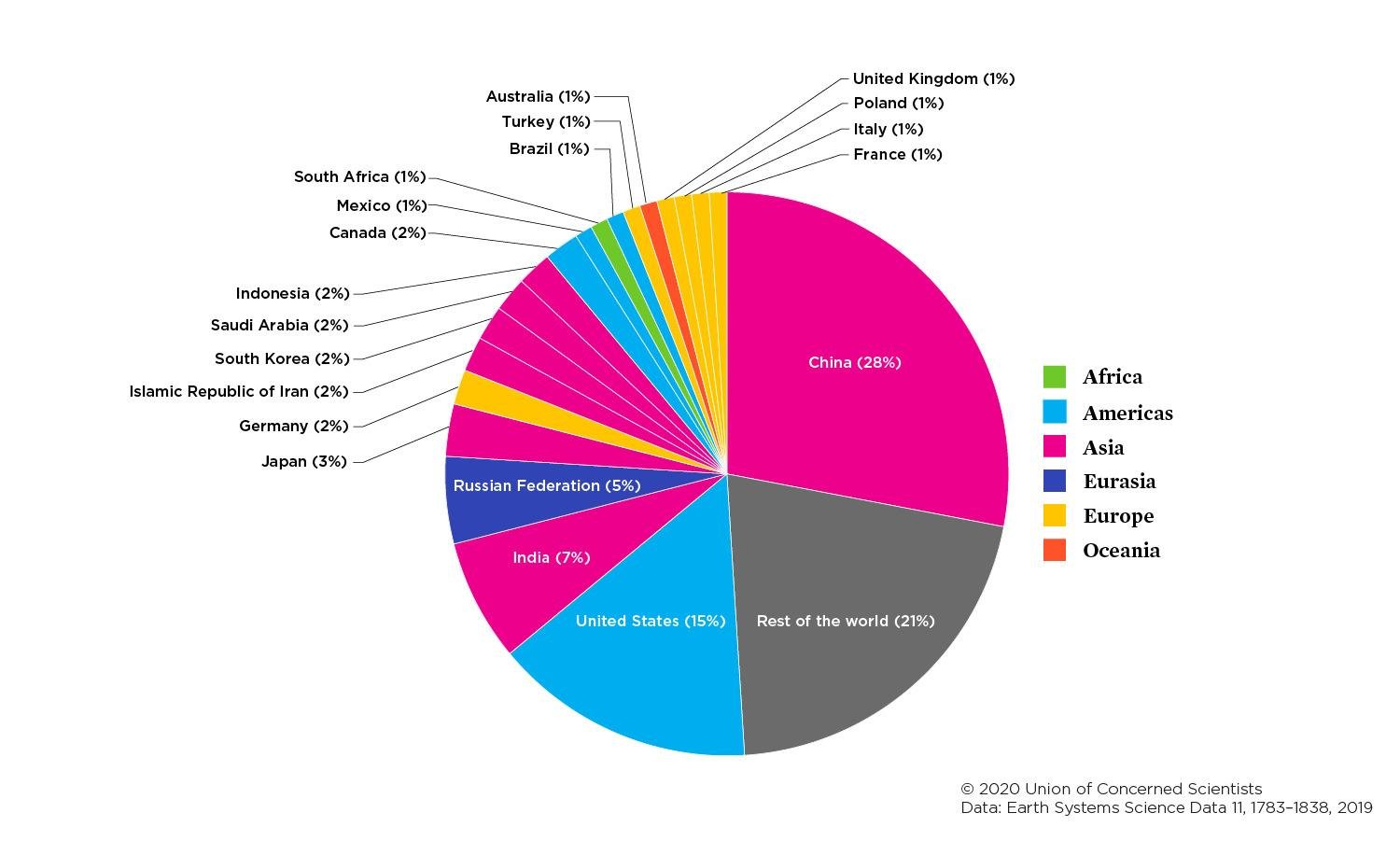



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists
Human activities and the greenhouse effect Human activities are increasing the amount of some greenhouse gases in the atmosphere For example farming cattle releases methane Human activities produce large amounts of greenhouse gases (GHGs), primarily carbon dioxide (CO 2), and thus contribute to global warmingThe use of fossil fuels is the primary source of CO 2 emissions, but the removal of trees from forested land has also contributed Mature forests, having absorbed CO 2 from the atmosphere while growing, store carbon in wood,Nitrous oxide is a powerful greenhouse gas that lasts for over 100 years in the atmosphere It is best known as laughing gas, but that kind of commercial use makes up only a tiny part of our emissions By far the biggest way we add nitrous oxide to the atmosphere is by growing crops with nitrogenbased fertilizers CFCs Up to 12,690




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
This imbalance between greenhouse gas emissions and the ability for natural processes to absorb those emissions has resulted in a continued increase in atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere have increased by about 40% since the mid1800sThe enhanced greenhouse effect What has scientists concerned now is that over the past 250 years, humans have been artificially raising the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at an everincreasing rate, mostly by burning fossil fuels, but also from cutting down carbonabsorbing forestsAtmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it the amount of CO2 might trigger glacial advances and retreats GS Callendar in 1938 solved a set of equations linking



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Main Sources What S Your Impact



Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere through a process called the greenhouse effect Having some greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is natural Their heattrapping abilities keep Earth from being uncomfortably cold However, the amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere has increased over the past 150 years as people burn fossil🔴 Answer 2 🔴 on a question Explain how changing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere affects the flow of heat out of Earth's atmosphere the answers to ihomeworkhelperscom The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,




The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases
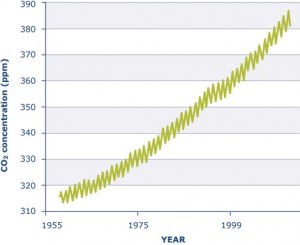



Lakes Climate Change Lake Scientist
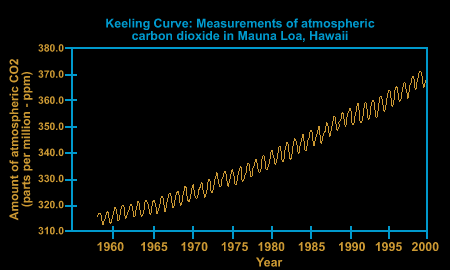
Carbon Footprint ↑ Amount of greenhouse gases released to the atmosphere as a result of our daily activities It is measured in equivalent tonnes of CO 2 per person and year Carbon Capture and Storage ↑ Naturebased process by which CO 2 is taken from the atmosphere and stored in a safe location (like geological formations) where it isSource EPA's Climate Change Indicators (16) Scientists have carefully examined all this evidence and made a startling discovery There's more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere now than at any other time in at least 650,000 years!Very roughly, each doubling of atmospheric carbon dioxide has the same effect on surface temperature Going from the level of carbon dioxide in the air before the industrial revolution, 280 parts per million by volume (280 ppm) to twice that, 560 ppm, and




Global Warming




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
Methane, by contrast, is mostly removed from the atmosphere by chemical reaction, persisting for about 12 years Thus although methane is a potent greenhouse gas, its effect is relatively shortlived Measurements of greenhouse gases (GHGs), whether performed in the atmosphere, or over terrestrial or marine ecosystems, have led to a fundamental understanding of the Earth System during the last century Nevertheless, we still do not fully understand global greenhouse gas cycling Up to date measurements of GHG are still rare (as observation Of the total amount of greenhouse gasses emitted, carbon dioxide covers 76% of the entire volume of gasses hence it is the highest volume of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere Methane It is an attractive fuel found on the ground and the sea floor, but when it escapes to the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane




Greenhouse Gas Wikiwand




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
Climate experts say the world must stop adding to the total amount of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere by 50, and that can only be done by drastically reducing the burning of fossil fuels as soon as possible, among other measures The report, which was released days before a UN climate summit begins Oct 31 in Glasgow, found most major oil and gas producersAtmosphere lead to temperature increases The amounts of greenhouse gases in the global atmosphere are clearly changingSome evidences of these changes fo r carbon dioxide and CFC11 in recent years are given in the following table The values are the mean for June each year at Cape Grim (Tasmania, Australia)Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6




V1003 Science And Society Sources And Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnes They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor Carbon dioxide Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) cooler




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




What Is Nitrous Oxide And Why Is It A Climate Threat Inside Climate News
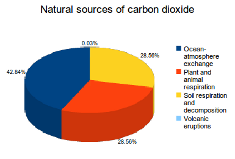
Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factors Dear EarthTalk Could it really be true that a single large volcanic eruption launches more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere than the amount generated by all of humanity over history?Water Vapour Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases Sources As greenhouse gases are essential for the existence of life, they are present in the atmosphere in a trace amount Natural sources of GHGs are volcanos, respiration by living organisms, decay and combustion of organic matter, etc




25 Wonderful Ways To Reduce Greenhouse Gases Conserve Energy Future



Greenhouse Gases
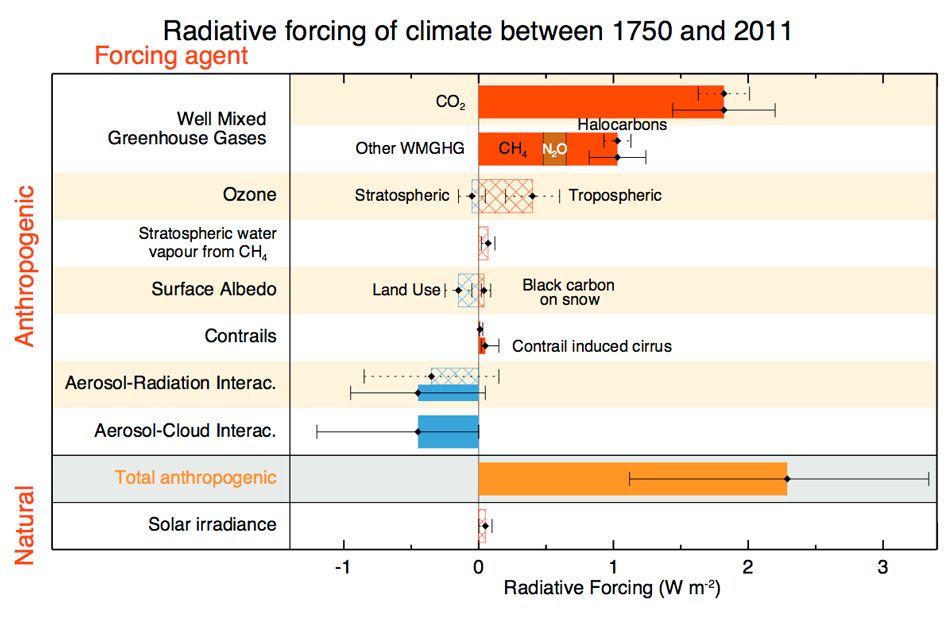
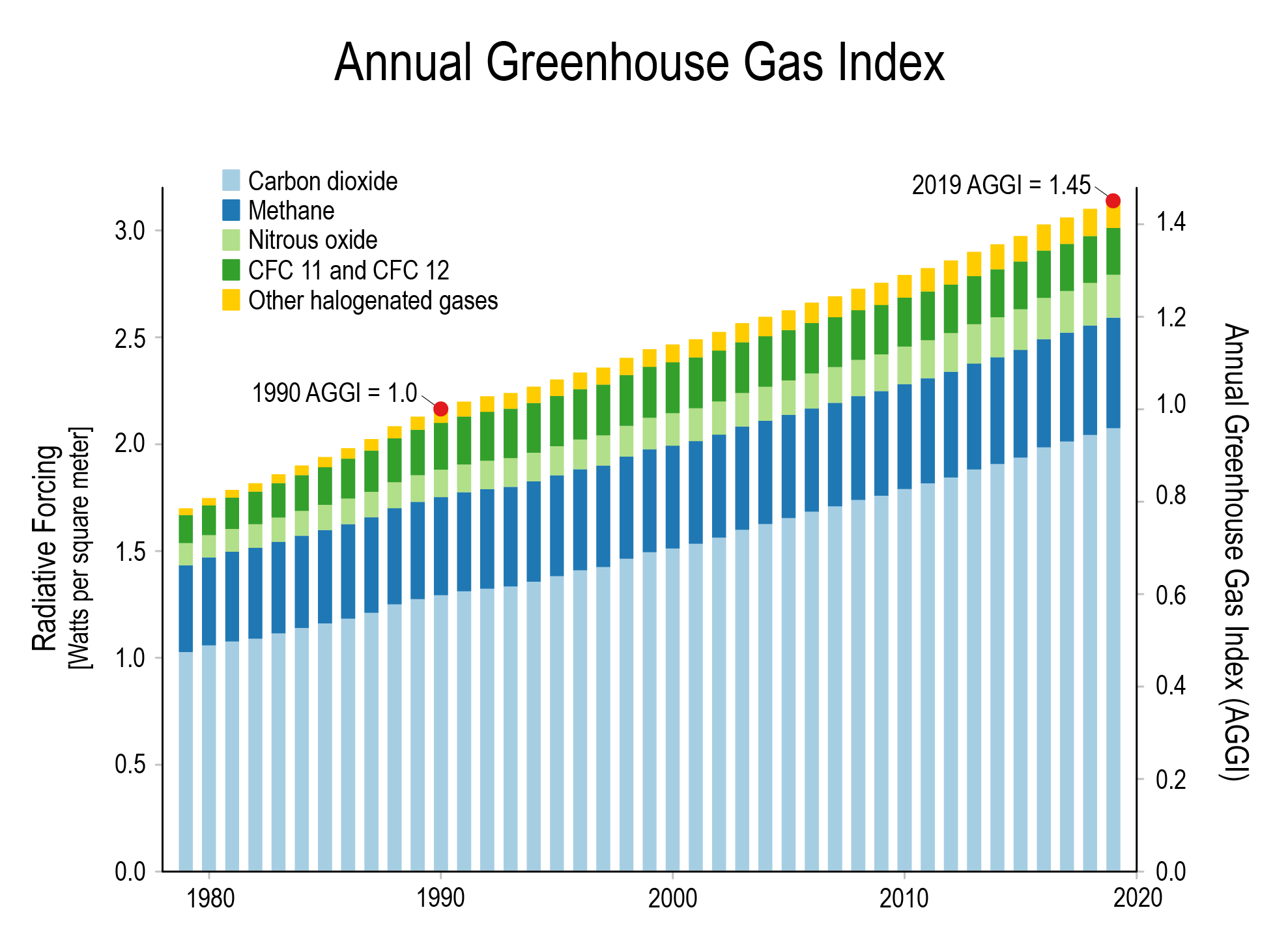
Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRL According to the 19 AGGI report, the combined heating influence of the longlived, humanproduced greenhouse gases is 314 Watts for every square meter of Earth's surface Just over 80 percent of that is due to carbon dioxide (66%) and methane (16%)Greenhouse gases and global warming Carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other greenhouse gases act like a blanket, absorbing IR radiation and preventing it from escaping into outer space The net effect is the gradual heating of Earth's atmosphere and surface, a Water vapor is the greenhouse gas with the highest concentration For this reason, it causes about 2/3 of the greenhouse effect, trapping the infrared radiation within its molecules Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide produces about 15% of the greenhouse effect and interacts with the atmosphere for both natural and anthropic causes



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Atmospheric Concentrations Fluorocarbons



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
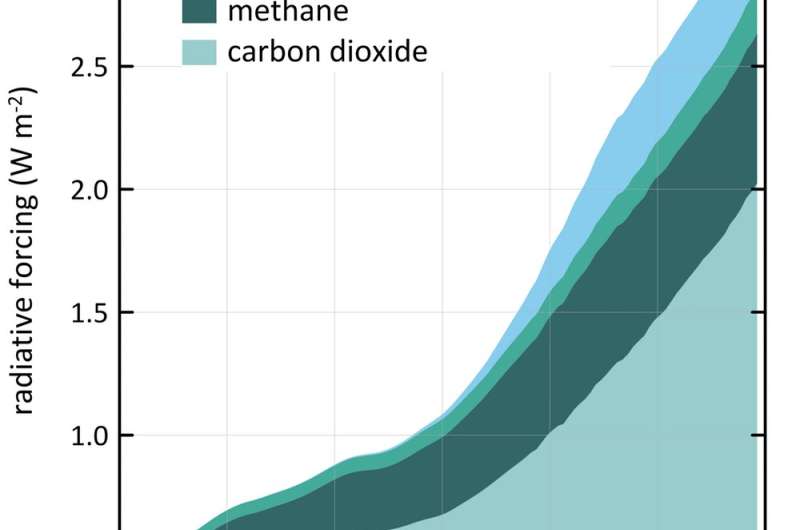



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Were Stopped Would The Climate Return To The Conditions Of 0 Years Ago Royal Society
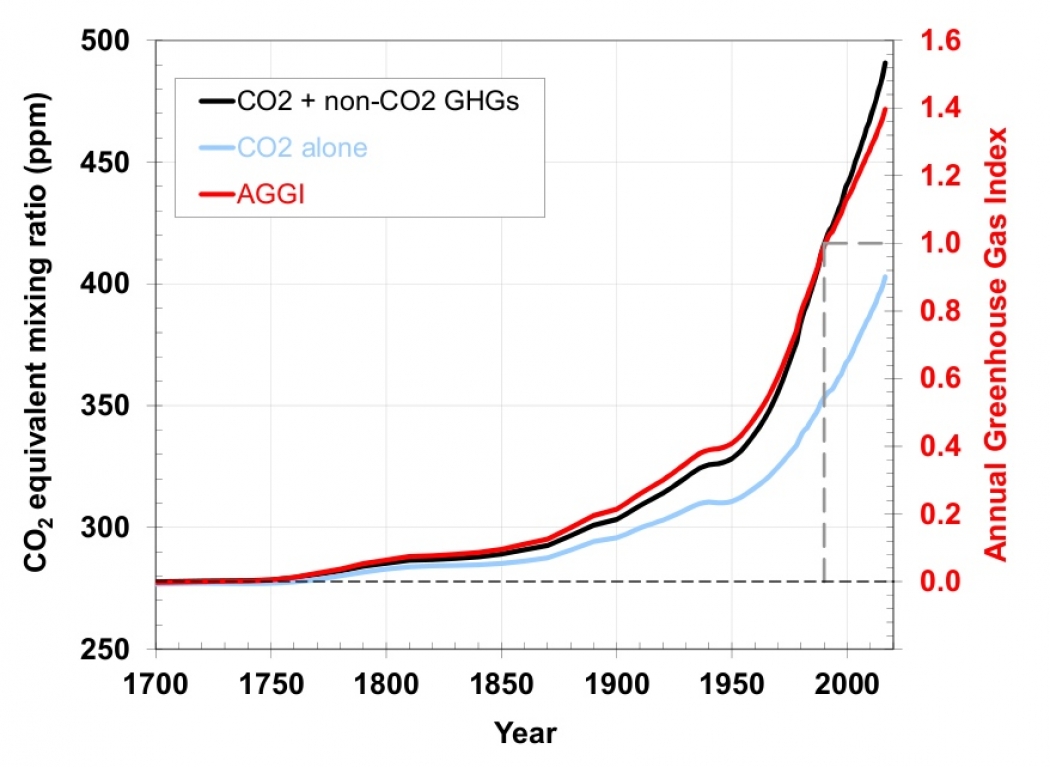



Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
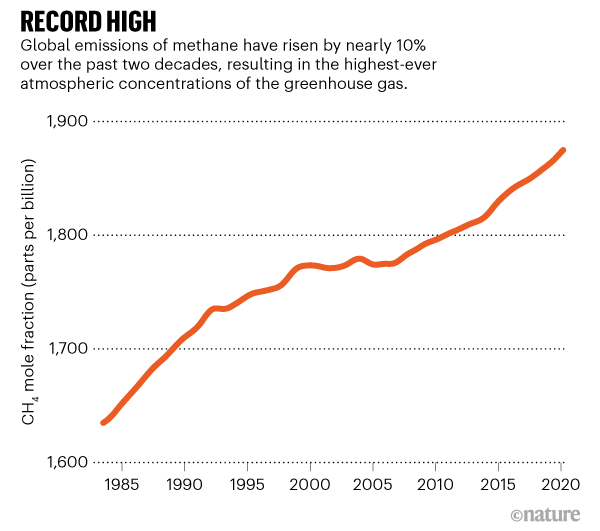



Global Methane Levels Soar To Record High




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov



1



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




From Atmospheric Observations And Analysis Of Greenhouse Gases To Emission Estimates A Scientific Adventure World Meteorological Organization



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data



Greenhouse Gas Basics 148 Msu Extension




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
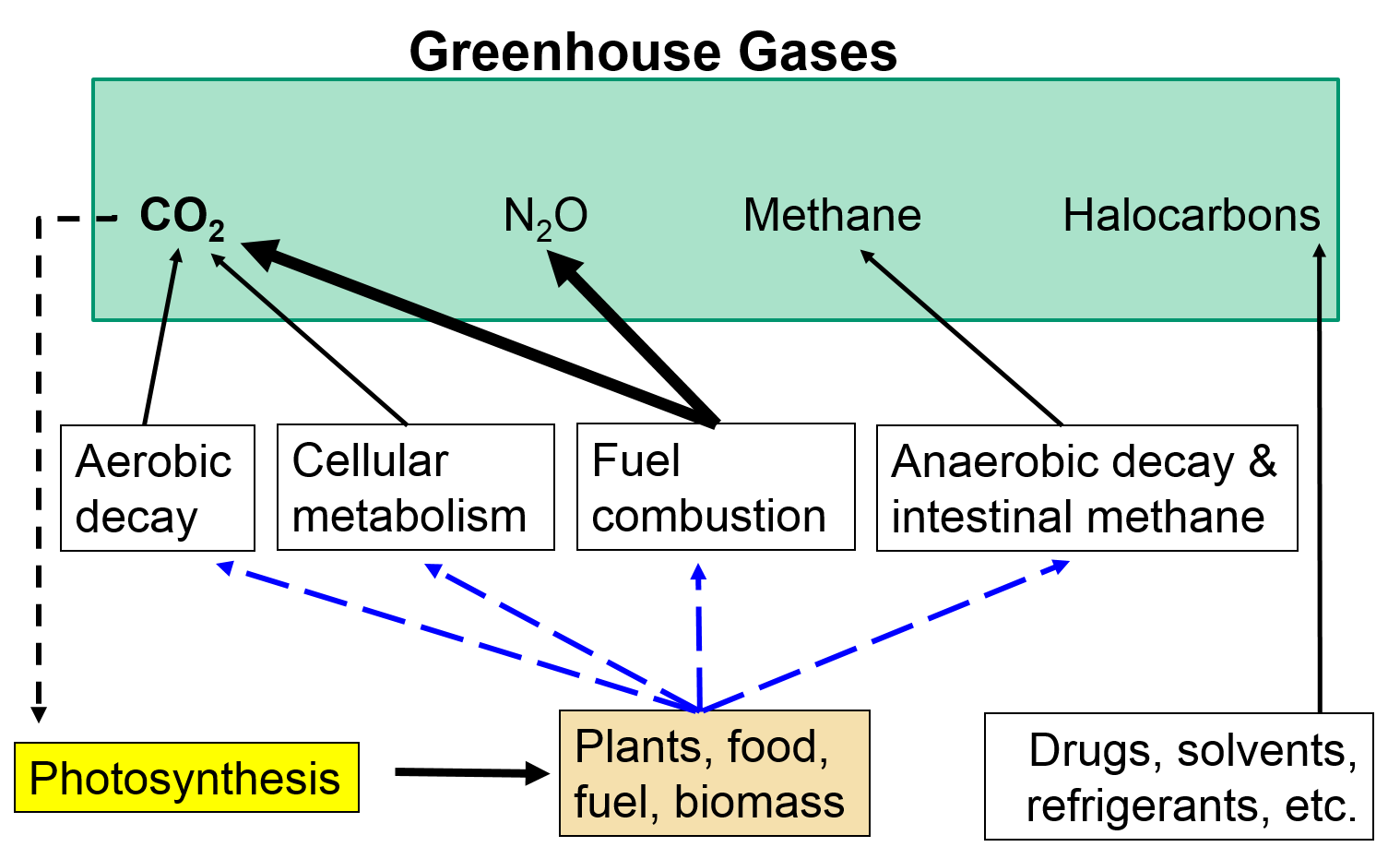



Greenhouse Gases Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




The Greenhouse Gases Airclim
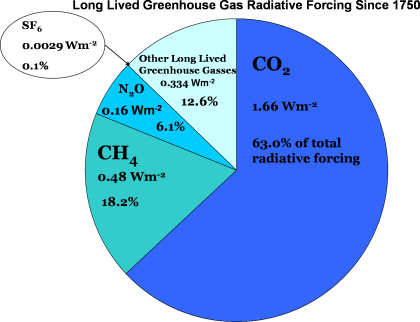



Noaa Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Hit New High Un



Atmo336 Spring 21



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
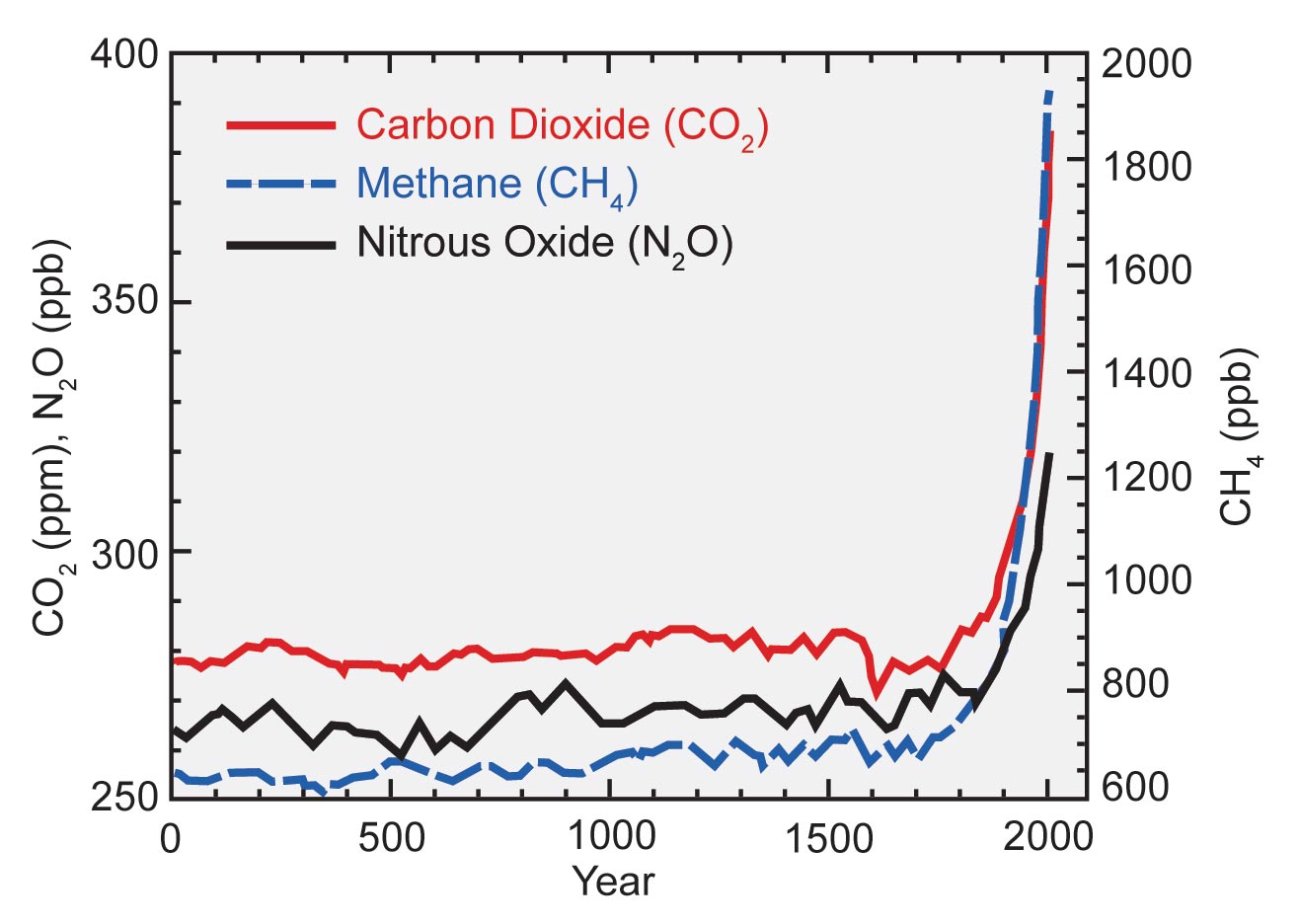



Climate Literacy Quiz




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record United Nations Sustainable Development



Changes In Concentration Of Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Other Greenhouse Gases And Aerosols
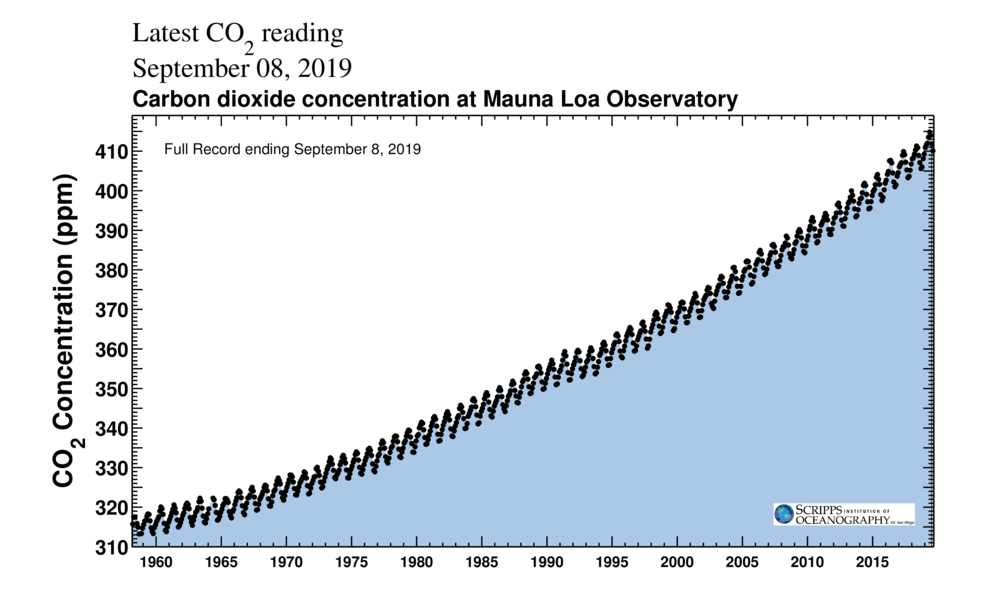



Climate Explained Why Carbon Dioxide Has Such Outsized Influence On Earth S Climate




Percentage Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Download Scientific Diagram




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Annual Ghg Index Aggi



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre
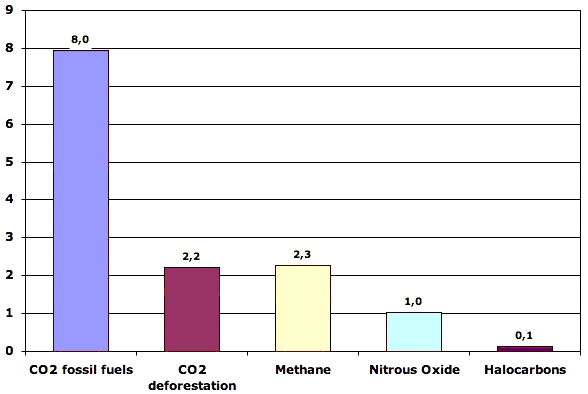



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Are Humans Causing Or Contributing To Global Warming Noaa Climate Gov




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature



The Greenhouse Effect




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov



Layers



Greenhouse Gases




Climate Chronicles Chapter 1 Climate Science For The Rest Of Us Ans Conservation Blog




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students



1



1
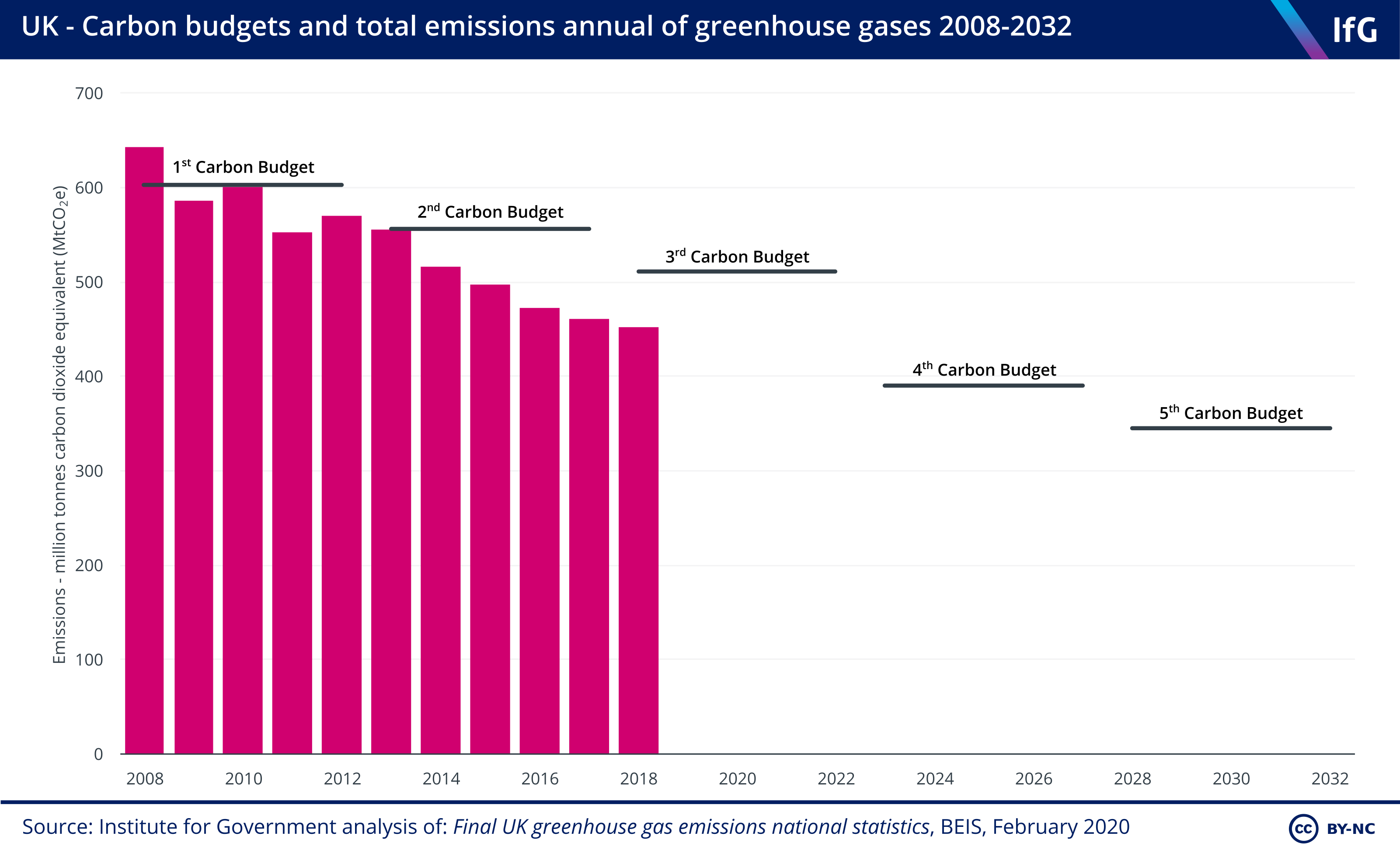



Uk Net Zero Target The Institute For Government



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
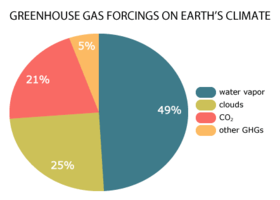



Which Are The Most Common Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Socratic



The Atmosphere Getting A Handle On Carbon Dioxide Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
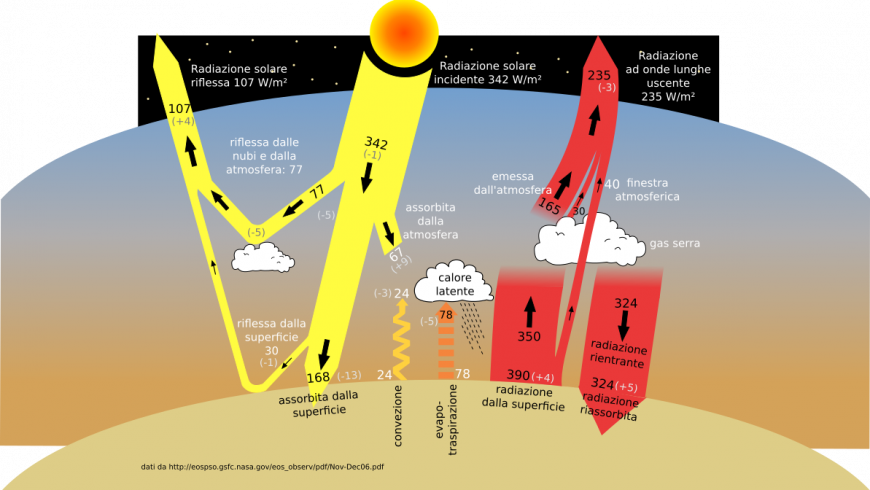



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions




Changes Since The Industrial Revolution American Chemical Society
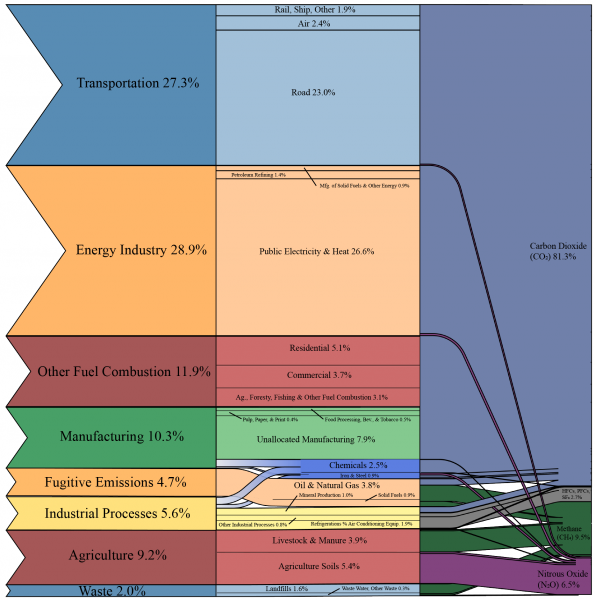



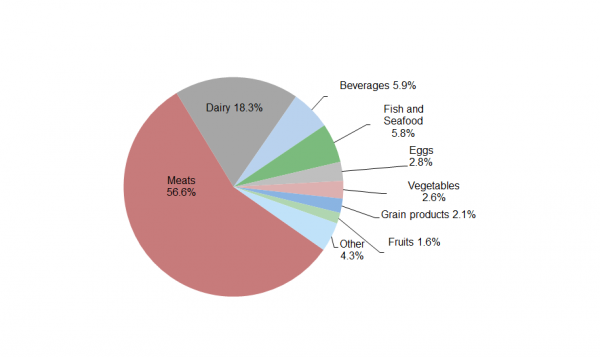
Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
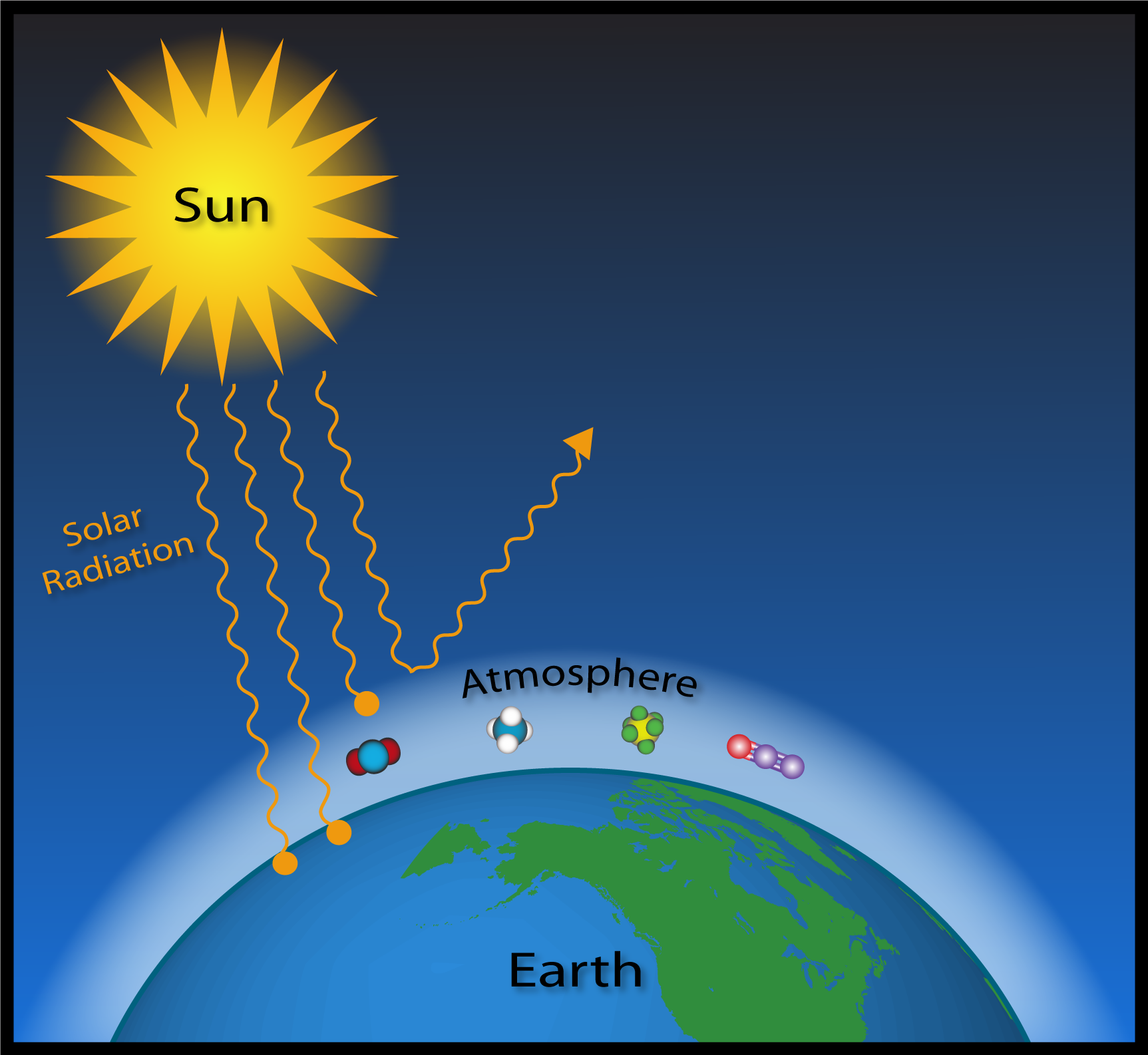



Greenhouse Gasses Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail U S National Park Service
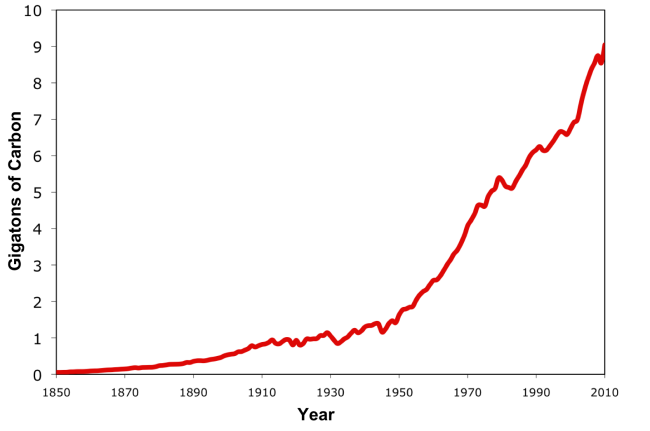



Noaa Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Why Earth Is Warming Ucar Center For Science Education
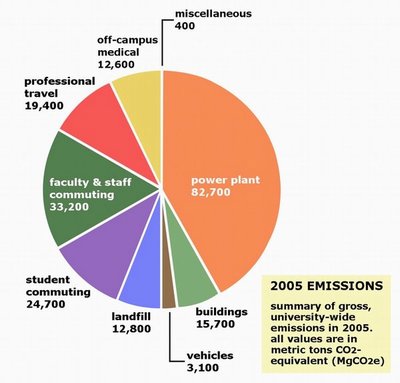



Uw Greenhouse Gases Down 10 Percent From 01 To 05 Inventory Finds Uw News




Percentage Share Of Greenhouse Gases In The Earth Atmosphere 5 Download Scientific Diagram
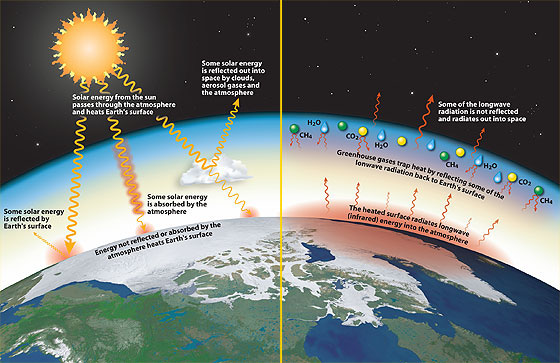



Too Much Of A Good Thing




Greenhouse Gases Must Be Scrubbed From The Air The Economist




Greenhouse Gas Amounts In Atmosphere Hit Record High Explained News The Indian Express



The Atmosphere Getting A Handle On Carbon Dioxide Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gases And The Atmosphere Science Learning Hub




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
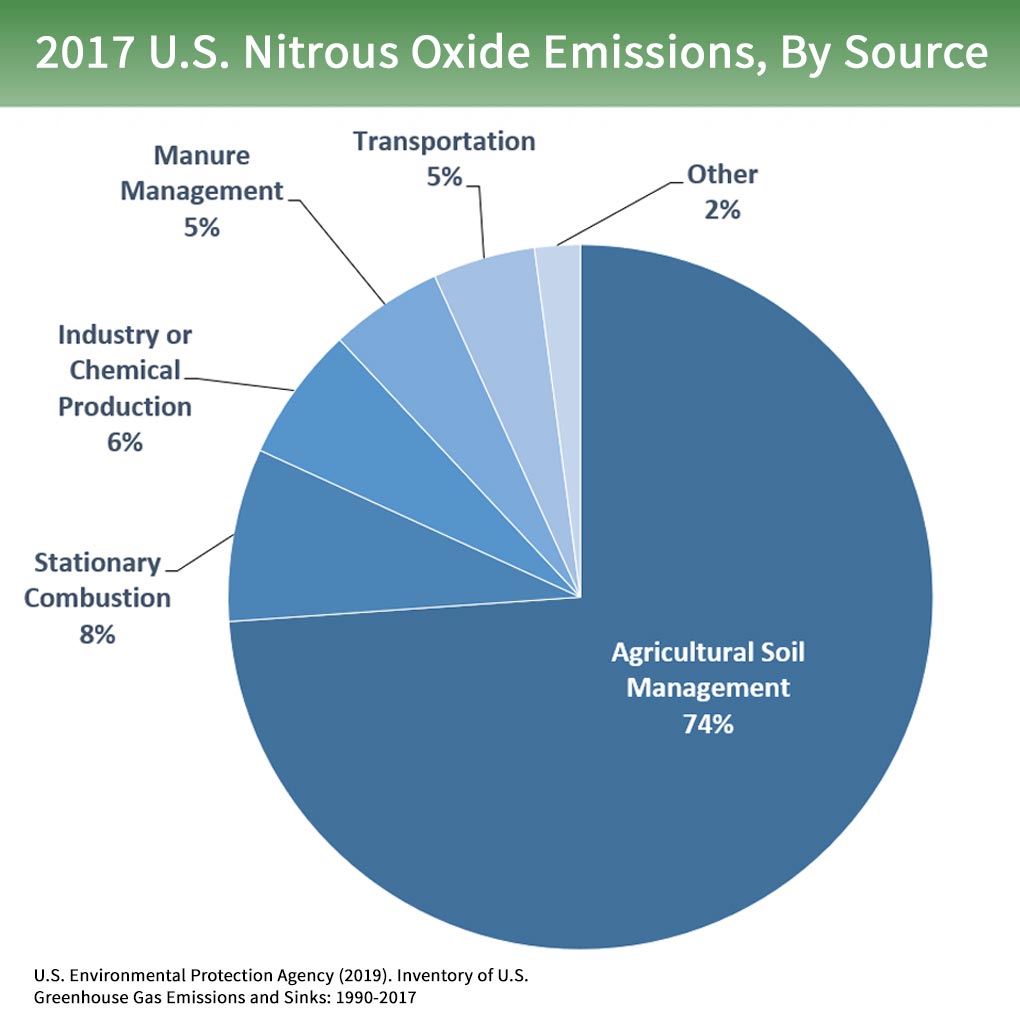



The Greenhouse Gas No One S Talking About Nitrous Oxide On Farms Explained Civil Eats



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
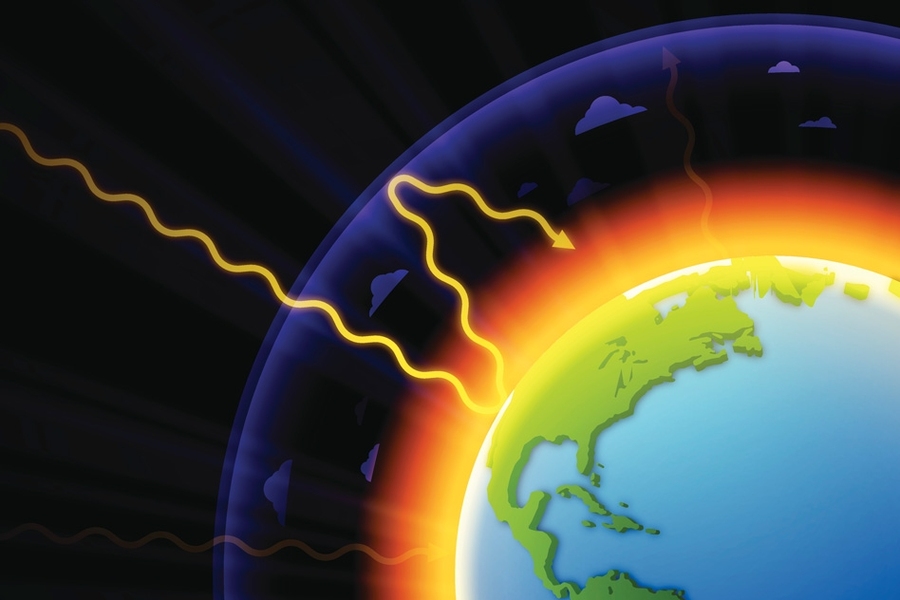




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




Greenhouse Effect And Historical Emissions
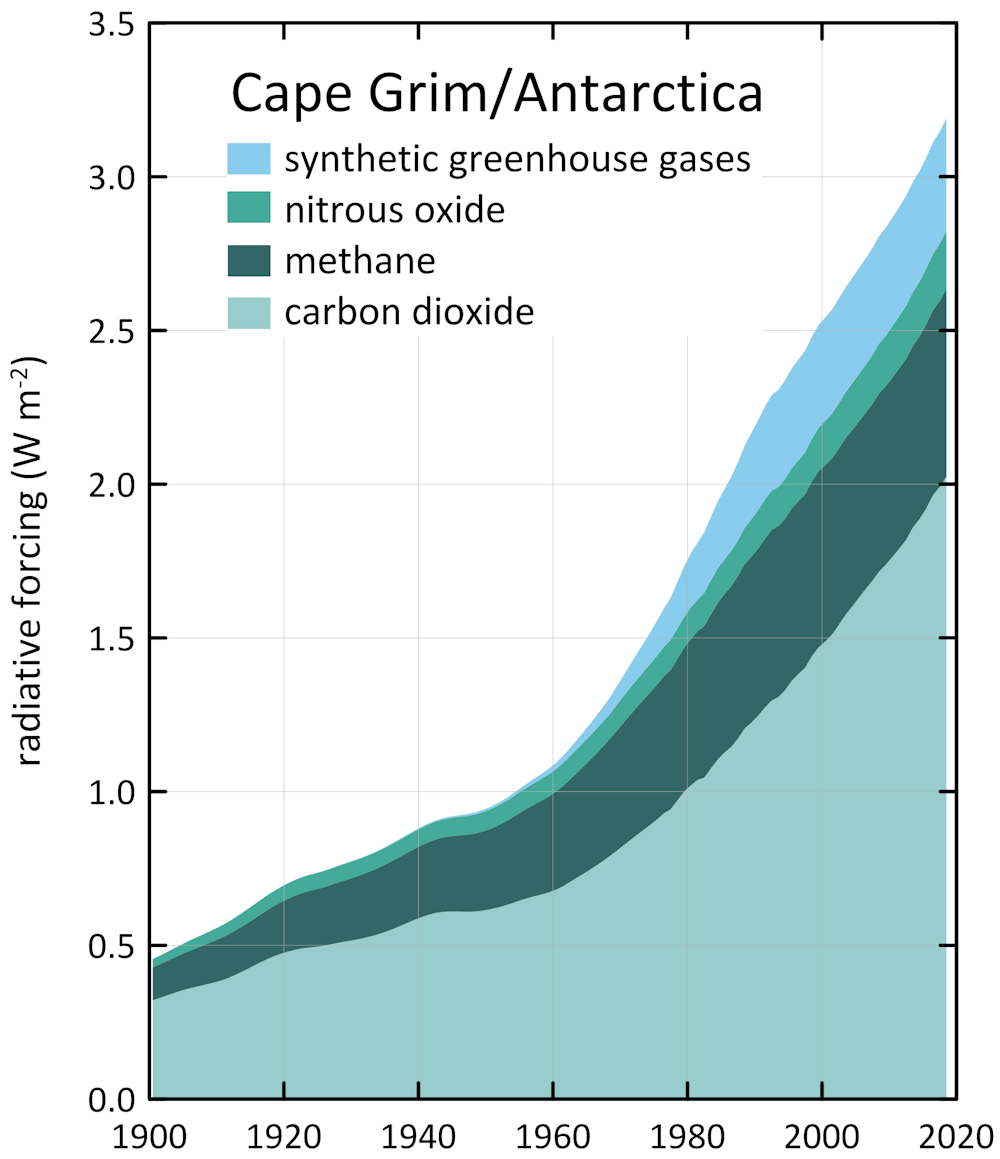



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
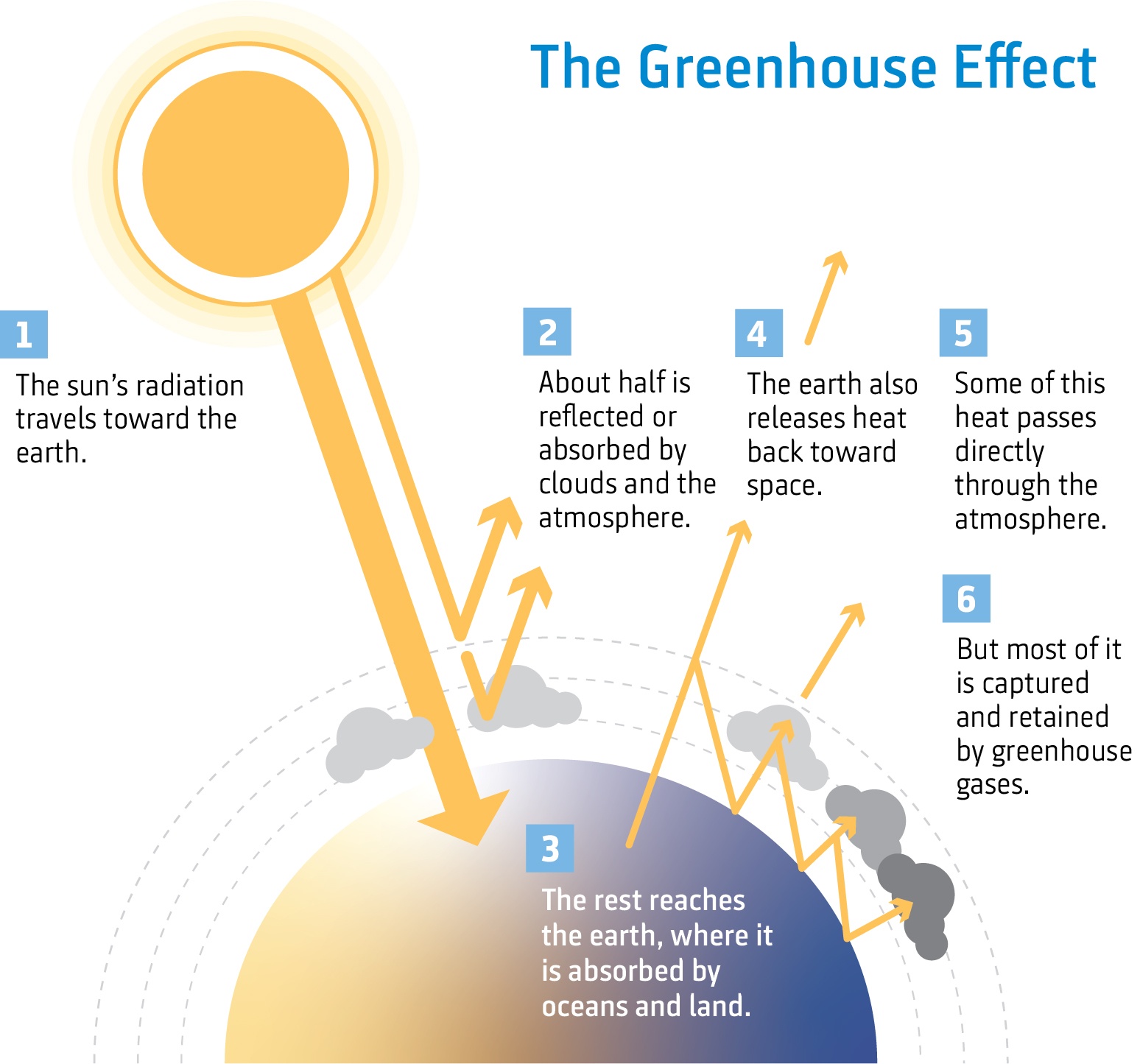



Climate Change The Science Niwa




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
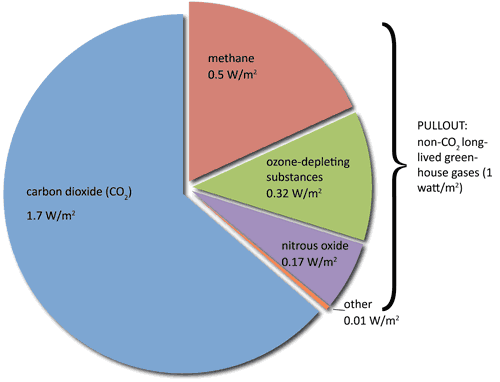



Greenhouse Gas It S Not Just About Co2




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science


